Product
Metal Scraps Products That We Offer
We supply high-quality ferrous, non-ferrous, and specialty metal scraps that power industries worldwide. Our products ensure sustainability, efficiency, and long-term value
FERROUS SCRAP
Heavy Melting Steel (HMS)
Ferrous scrap is any discarded or recycled material primarily composed of iron and steel.
Distinguished by its magnetism and durability, ferrous scrap is the most commonly recycled
material in the world and serves as a vital raw material for new metal production.
Ferrous metals are used in a vast range of products, and their scrap is often categorized
based on its source and composition.
- Heavy Melting Steel (HMS): Beams & industrial equipment.
- Cast Iron Scrap: Automotive & machinery parts
- Auto Scrap: Vehicles salvaged for steel/iron.
- Industrial/Prompt Scrap: Factory leftovers & by-products.
The recycling process
1) Collection: Ferrous scrap is collected from various sources, including demolition
sites, factories, and consumer goods
2) Sorting: Using large magnets, recycling facilities separate the magnetic ferrous
metals from non-ferrous metals like Aluminum and copper.
3) Processing: The sorted metal is shredded or sheared into smaller pieces to increase
its surface area, which makes melting more efficient.
4) Melting and Purification: Shredded ferrous scrap is melted in large furnaces, such as
an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). Impurities are removed to ensure the final product
meets quality standards.
5)Solidifying: The molten metal is cast into new shapes, such as bars, sheets, or ingots,
ready for manufacturers to use.
Applications
Recycled ferrous scrap is used to create new steel and iron products for many industries.
- Steel Production: Recycled scrap is a primary raw material for new steel products.
- Construction: Recycled steel is used for structural beams, rebar, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Automotive Industry: Steel from recycled sources is used to produce vehicle bodies, frames, and various engine components.
- Appliances: Manufacturers use recycled metal to produce new refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens.
- Machinery: Recycled ferrous metals are used for agricultural, industrial, and mining equipment.
Environmental and economic benefits
- Energy Conservation: Producing steel from recycled scrap uses significantly less energy than creating it from virgin iron ore. Some sources estimate savings of over 50%.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling reduces the need for mining iron ore, coal, and limestone, preserving finite natural resources and minimizing the environmental impact of mining.
- Reduced Pollution: The recycling process creates far less air and water pollution compared to the production of new steel from raw materials.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Recycling one ton of steel can cut carbon emissions by over 58%.
- Economic Impact: The recycling industry creates jobs and generates significant economic activity. It also offers cost-effective raw materials for manufacturers.
- Reduced Landfill Waste: Keeping scrap metal out of landfills prevents toxic substances from leaching into the soil and water.


LIGHT METAL SCRAP (LMS)
Ferrous light metal scrap" refers to relatively thin or light-gauge steel and iron scrap, such as sheet metal, pipes, and appliance parts, which are magnetic due to their iron content. While less dense than heavier ferrous metals, this type of scrap is highly valuable for recycling due to its widespread use in consumer goods and industrial applications, and its magnetic property allows for easy differentiation from non-ferrous metals.
LMS Ferrous
This term indicates the metal contains iron, making it magnetic and strong but also susceptible to rust and corrosion. This specifies the relatively thin or light gauge of the metal, distinguishing it from heavy or dense ferrous scrap like structural beams. This refers to discarded metal that can be collected, processed, and recycled.
NON-FERROUS SCRAPS (ALUMINIUM)
Aluminum UBC
Aluminium UBC, or Used Beverage Container, refers to the high-quality Aluminum scrap collected from recycled drink cans. This post-consumer material is a highly valuable commodity in the recycling industry due to its purity and endless recyclability.
1) Collection and sorting - Consumers deposit used cans in recycling bins and centers.
At a material recovery facility, magnets are used to separate aluminum cans from steel
cans and other materials.
2) Shredding. The sorted and baled cans are sent to a recycling plant, where a large
shredder breaks them into small, walnut-sized pieces. This increases the surface area
for the next stage.
3) De-coating. The shredded pieces are passed through a furnace where hot air is used to
remove any paint, lacquer, or other coatings. This step is crucial for removing
impurities that would affect the final product's quality.
4) Melting. The de-coated Aluminum shreds are fed into a melting furnace. Specialized
stirrers create a vortex that rapidly pulls the Aluminum into the molten pool,
preventing excessive oxidation and ensuring a high yield.
5) Casting. The purified molten Aluminum is poured into a mold, where it is cooled
with water to form large, solid blocks called ingots. One ingot can contain the metal
from approximately 1.5 million used cans.
6) Rolling and manufacturing. The ingots are sent to a rolling mill, where they are
heated and pressed into thin sheets of Aluminum coil. These sheets are then used by
can manufacturers to produce new Aluminum cans, completing the cycle in as little as
60 days.



Aluminium Extrusion 6063
Aluminium Extrusion 6063 Scrap is a valuable type of commercial Aluminum scrap typically sourced from window frames, door frames, and architectural structures. Its value is primarily determined by its purity and the presence of contaminants like paint, iron, or plastic.
Material composition:
The material is based on the 6063 Aluminum alloy, known for its corrosion resistance and good surface finish.
- Main elements: Silicon (Si) at 0.20–0.60% and Magnesium (Mg) at 0.45–0.90%.
- Contaminants: Iron (Fe) content should be a maximum of 0.35%, with other elements like copper, zinc, and manganese also tightly controlled.
Contaminant-free condition:
The highest price is commanded by "clean" or "bare" 6063 scrap, which is free of other metals, screws, plastic, and dirt.
International standards:
The Institute of Scrap Recycling Industries (ISRI) specifies grades for Aluminum scrap, and the code for 6063 extrusion scrap is TATA



Aluminium Alloy Wheels
Aluminium alloy wheels are vehicle wheels made from an alloy of aluminium mixed with other metals, like nickel or magnesium. Aluminium alloy wheel scrap, known by the ISRI code "TROMA," is a valuable, non-ferrous metal widely recycled for its high Aluminum content. The recycling process for Aluminum alloy wheels is highly energy efficient and has significant environmental benefits.
- Preparation and melting: At a recycling facility, the wheels are shredded and undergo magnetic separation to remove any remaining ferrous metals. The pure Aluminum is then melted down.
- Lower energy consumption: Recycling Aluminum uses only about 5% of the energy required to produce new Aluminum from bauxite ore. This translates to less air and water pollution.
- Resource conservation: Recycling helps conserve natural resources and reduces the need for extensive mining operations.
- Wheel-to-wheel recycling: Some companies have developed closed-loop "wheel-to- wheel" systems where old alloy wheels are collected, recycled, and used to manufacture new alloy wheels.



Aluminium Casting Scrap
Aluminium casting scrap is waste material from manufacturing processes or discarded products that is melted down and reused, which offers significant economic and environmental benefits. The value of the scrap depends on its purity and alloy composition.
- Preparation and melting: At a recycling facility, the wheels are shredded and undergo magnetic separation to remove any remaining ferrous metals. The pure Aluminum is then melted down.
- Lower energy consumption: Recycling Aluminum uses only about 5% of the energy required to produce new Aluminum from bauxite ore. This translates to less air and water pollution.
- Resource conservation: Recycling helps conserve natural resources and reduces the need for extensive mining operations.
- Wheel-to-wheel recycling: Some companies have developed closed-loop "wheel-to- wheel" systems where old alloy wheels are collected, recycled, and used to manufacture new alloy wheels.
- Clean casting scrap: This is free of contamination like paint, steel, or non-metallic parts. Because it requires minimal processing, it is one of the most valuable grades.
- Dirty or mixed casting scrap: This contains non-metallic components like steel bolts or rubber bushings, or has been painted or coated. It must be sorted and cleaned before being recycled, which lowers its value.
- Diecast scrap: This is generated specifically from die-casting operations and includes defective products or off-cuts. Its alloy content can vary significantly depending on the industry.
- Automotive scrap: A significant source of casting scrap is discarded vehicle parts, such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission cases.



Aluminium Ingots – A7 Grade
a high-purity, primary Aluminum grade prized for their versatility, quality, and specific chemical composition. The designation "A7" signifies a minimum Aluminum content of 99.7%. The ingots are produced through the smelting and casting of refined alumina derived from bauxite ore.
- High purity: A minimum of 99.7% Aluminum content with very low levels of impurities like iron (Fe) and silicon (Si).
- Lightweight: Like other Aluminum products, A7 offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is crucial for reducing mass in manufacturing applications.
- Corrosion resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that shields the metal from the elements, ensuring long-term durability.
- High thermal and electrical conductivity: These properties make A7 suitable for components requiring efficient heat dissipation or electrical transmission.
- Recyclability: Aluminum is highly sustainable and can be recycled repeatedly without a loss in quality, making A7 an environmentally friendly choice.
- Malleability and formability: The material can be easily shaped and formed for various manufacturing processes.


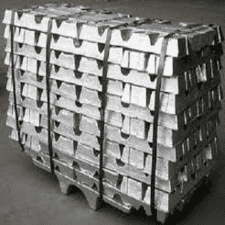
Copper Cathode
A copper cathode is a form of high-purity copper produced through the electrolytic refining of copper ore. These large, rectangular plates, with a typical purity of 99.99%, serve as the primary raw material for manufacturing a wide range of copper products.
The production of copper cathodes involves several stages, which differ depending on the type of copper ore (sulphide or oxide).
- Mining and concentration:Copper ore is first extracted from a mine, crushed, and ground into a powder. The copper-containing minerals are then concentrated into a slurry.
-
For oxide ores (hydrometallurgy):>
The concentrated ore undergoes leaching, where a weak acid solution dissolves, the copper content .
The resulting copper-rich solution is then treated in a process called electrowinning. An electric current causes pure copper to deposit onto starter cathode plates, resulting in a high-purity product. - The concentrated ore undergoes leaching, where a weak acid solution dissolves the copper content.
- The resulting copper-rich solution is then treated in a process called electrowinning. An electric current causes pure copper to deposit onto starter cathode plates, resulting in a high-purity product.
- For sulphide ores (pyrometallurgy):>
- The concentrated ore is processed in a smelter at high temperatures to produce blister copper, which is about 99% pure.
- This blister copper is cast into large anodes and placed in an electrolytic bath.
- Through electrolytic refining, an electric current moves copper ions from the impure anode to the pure copper starter sheet (the cathode). Impurities settle to the bottom as "anode slime".



Stainless Steel Scrap
Stainless Steel SS304 & SS316 scrap is a valuable, non-magnetic scrap metal that is widely recycled for its high nickel and chromium content. The price fluctuates based on global commodity markets and the scrap's quality.
SS 304
- Corrosion resistance: Grade 304 is composed of approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which provides excellent resistance to corrosion.
- Recyclability: It is 100% recyclable. Recycling stainless steel reduces the need for virgin materials and helps cut down on energy consumption during manufacturing.
- High alloy content: The nickel and chromium content are valuable in the scrap metal market and fetch a higher price than common ferrous scrap.
SS 316
Stainless steel 316 scrap is a valuable, non-magnetic scrap metal known for its high corrosion resistance, which is primarily due to its molybdenum content. This makes it more valuable than the more common 304 stainless steel. It can be recycled for use in various industries, including marine, chemical processing, and medical manufacturing.
- Composition: 316 stainless steel contains 16–18% chromium, 10–14% nickel, and most importantly, 2–3% molybdenum. It is the added molybdenum that sets it apart from grade 304, providing superior resistance to chlorides and other corrosive chemicals.
- Higher value: Because of its higher nickel content and the presence of molybdenum, 316 stainless steel scrap fetches a higher price than 304 grade.
- Non-magnetic: As an austenitic stainless steel, grade 316 is non-magnetic. You can use a magnet to help confirm its non-magnetic properties, which distinguishes it from lower-value, magnetic stainless-steel grades like 430
- Testing for molybdenum: If you are unsure whether a piece of stainless steel is 304 or 316, you can purchase a molybdenum test kit. The test involves applying a testing solution that reacts with the molybdenum in 316, causing a brown stain to appear. If it is 304, there will be no reaction.


EXCLUSIVE COMMODITIES
Premium Global Products
Jasmine Thai Rice
Thai Jasmine rice is a long-grain rice variety famous for its distinct floral aroma, soft texture, and slightly sweet flavour. It is a staple of Thai cuisine and an important export crop.
- Aroma: The signature fragrance is caused by the compound 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, which is also found in pandan leaves. It is often described as resembling pandan or popcorn.
- Texture: When cooked, the grains are tender and moist with a soft, slightly sticky texture that clings together but is not as sticky as glutinous rice.
- Flavour: It has a subtle, nutty, and slightly sweet flavour.
- Appearance: Uncooked grains are long and slender. The term "Jasmine" likely refers to the color of the cooked rice, which is white like the jasmine flower, rather than the scent.
- Vitamins: Contains B vitamins like thiamin (B1), niacin (B3), and pyridoxine (B6), which help convert food into energy.
- Minerals: Includes magnesium, manganese, iron, and selenium.
- Antioxidants: Colourful varieties of jasmine rice contain phytonutrients and antioxidants that protect cells from damage.


Sugar ICUMSA 45
ICUMSA 45 Sugar is widely recognized as one of the highest-quality sugars available
on the market. Known for its exceptional purity and consistent white color, it is a
highly refined, granulated sugar suitable for various food and beverage industry
uses. ICUMSA Sugar undergoes stringent processing to ensure it meets the highest
standards, making it ideal for consumption and industrial applications. Its versatility
and quality make it a preferred choice for manufacturers, retailers, and consumers
worldwide.
Topson Global Group Company sources best quality Sugar from the renowned sugar
factories in Thailand, for export to various countries.

Industrial Grade Urea
Industrial grade urea, also known as technical grade urea, is a refined form of the organic compound primarily used for non-agricultural industrial applications. Unlike agricultural-grade urea, which is often treated with chemicals for slower release as a fertilizer, industrial grade urea is processed to a higher level of purity. This higher purity and more consistent composition make it suitable for manufacturing processes with tight specifications.
- Appearance: A white crystalline solid or powder.
- Purity: Contains fewer impurities, especially lower levels of biuret, than agricultural grades. Biuret can be toxic to some plants and interfere with certain industrial reactions.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water.
- Nitrogen content: High nitrogen content, typically around 46%.
- Hygroscopic: Readily absorbs moisture from the air.
Within the industrial category, even higher-purity grades exist for more sensitive uses:
- Automotive Grade Urea (DEF): A high-purity, 32.5% urea solution used in Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in diesel engines.


Our Customers’ Feedback
Topson Global Group has truly transformed the way we approach scrap metal sourcing. Their transparency, prompt delivery, and ethical practices set them apart. We have full confidence in their team and the quality they deliver
From our first interaction, Topson Global stood out. Their leadership’s expertise and long-term vision show in every deal—responsive, fair and always professional
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Topson Global Group Co., Ltd is a scrap metals & commodities trading company based in Bangkok, Thailand. They buy and sell scrap metals and related commodities and aim to build global, ethical, and transparent supply chains in this industry
They are headquartered in Bangkok, Thailand, operating in the ASEAN region
Emphasis on ethical and transparent trading
Building long-term relationships with clients and partners
Visionary and experienced leadership
They trade in scrap metals and commodities. The “Services” section suggests involvement in supply chain building, procurement, and trading. (Note: Some parts of the website as seen had placeholder/lorem ipsum text under certain repair or automotive services – likely template content, not actual services offered.)

